In this blog post, I’ll walk through the development of a robust banking application built with Node.js, TypeScript, and MongoDB. This application follows domain-driven design principles and implements a clean, layered architecture to manage bank accounts and transactions.
Technologies Used
Core Technologies
- Node.js: Server-side JavaScript runtime
- TypeScript: Adds static typing to JavaScript, enhancing code quality and developer experience
- MongoDB: NoSQL database for flexible data storage
- Mongoose: ODM (Object Data Modeling) library for MongoDB and Node.js
- Express: Web framework for building RESTful APIs
- Swagger/OpenAPI: API documentation and testing interface
Development Tools
- Docker & Docker Compose: Containerization for consistent development and deployment
- Jest: Testing framework for unit and integration tests
- ESLint & Prettier: Code quality and formatting tools
- Git: Version control system
Architecture Overview
The application follows a clean, layered architecture inspired by Domain-Driven Design (DDD) principles:
src/
├── api/ # API Layer (Controllers, Routes, Middleware)
├── application/ # Application Services Layer
├── domain/ # Domain Layer (Entities, Value Objects, Domain Services)
└── infrastructure/ # Infrastructure Layer (Database, External Services)
Architecture Diagram
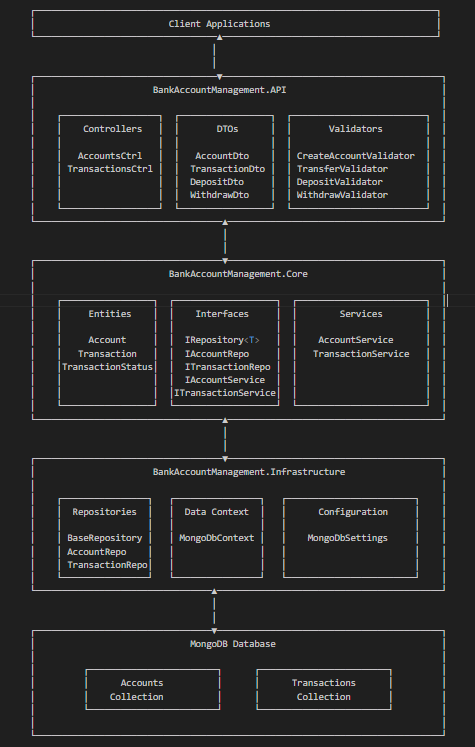
Domain Layer
The domain layer contains the core business logic and entities:
- Entities: Account and Transaction classes that encapsulate business rules
- Value Objects: Money class for handling currency and amounts
- Domain Services: AccountService for business operations like transfers
Application Layer
The application layer orchestrates the use cases:
- Application Services: Coordinates domain objects to fulfill use cases
- DTOs: Data Transfer Objects for input/output transformation
Infrastructure Layer
The infrastructure layer handles external concerns:
- Database: MongoDB connection and Mongoose schemas
- Repositories: Data access patterns for domain entities
API Layer
The API layer exposes the functionality to clients:
- Controllers: Handle HTTP requests and responses
- Routes: Define API endpoints
- Middleware: Request validation, error handling, etc.
- Swagger: API documentation and testing
Key Features
Account Management
- Create new bank accounts
- Retrieve account details and balance
- List all accounts
Transaction Processing
- Deposit funds to accounts
- Withdraw funds from accounts
- Transfer funds between accounts
- View transaction history
Data Validation
- Input validation using middleware
- Business rule validation in domain layer
Error Handling
- Centralized error handling
- Meaningful error messages
Implementation Highlights
Domain Entities
The Account entity encapsulates the core business logic for accounts:
export class Account {
private \_id: string;
private \_name: string;
private \_balance: Money;
constructor(id: string, name: string, balance: Money) {
this.\_id = id;
this.\_name = name;
this.\_balance = balance;
}
// Business methods
deposit(amount: Money): void {
if (amount.value <= 0) {
throw new Error('Deposit amount must be positive');
}
this.\_balance = this.\_balance.add(amount);
}
withdraw(amount: Money): void {
if (amount.value <= 0) {
throw new Error('Withdrawal amount must be positive');
}
if (this.\_balance.value < amount.value) {
throw new Error('Insufficient funds');
}
this.\_balance = this.\_balance.subtract(amount);
}
}Value Objects
The Money value object ensures consistent handling of monetary values:
export class Money {
private readonly \_value: number;
constructor(value: number) {
this.\_value = Math.round(value \* 100) / 100; // Round to 2 decimal places
}
get value(): number {
return this.\_value;
}
add(money: Money): Money {
return new Money(this.\_value + money.value);
}
subtract(money: Money): Money {
return new Money(this.\_value - money.value);
}
}Domain Services
The AccountService handles operations involving multiple accounts:
export class AccountService {
transfer(fromAccount: Account, toAccount: Account, amount: Money): void {
if (amount.value <= 0) {
throw new Error('Transfer amount must be positive');
}
fromAccount.withdraw(amount);
toAccount.deposit(amount);
}
}Repository Pattern
Repositories abstract the data access logic:
export class AccountRepository implements IAccountRepository {
async findById(id: string): Promise<Account | null> {
const accountDoc = await AccountModel.findById(id);
if (!accountDoc) return null;
return new Account(
accountDoc._id.toString(),
accountDoc.name,
new Money(accountDoc.balance)
);
}
async save(account: Account): Promise<void> {
await AccountModel.findByIdAndUpdate(
account.id,
{
name: account.name,
balance: account.balance.value
},
{ upsert: true }
);
}
}API Controllers
Controllers handle HTTP requests and delegate to application services:
export class AccountController {
constructor(private accountService: AccountService) {}
async createAccount(req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> {
const { name } = req.body;
const account = await this.accountService.createAccount(name);
res.status(201).json(account);
}
async getAccount(req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> {
const { id } = req.params;
const account = await this.accountService.getAccount(id);
if (!account) {
res.status(404).json({ message: 'Account not found' });
return;
}
res.status(200).json(account);
}
}Database Design
The MongoDB database uses two main collections:
Accounts Collection
{
_id: ObjectId,
name: String,
balance: Number
}Transactions Collection
{
_id: ObjectId,
type: String, // 'DEPOSIT', 'WITHDRAWAL', 'TRANSFER'
amount: Number,
fromAccountId: ObjectId, // For transfers
toAccountId: ObjectId, // For deposits and transfers
timestamp: Date
}Docker Setup
The application uses Docker Compose to run MongoDB and MongoDB Express:
version: '3.8'
services:
mongo:
image: mongo:latest
container_name: banking-mongodb
restart: always
ports: - "27017:27017"
environment: - MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin - MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password
volumes: - mongodb-data:/data/db
networks: - banking-network
mongo-express:
image: mongo-express:latest
container_name: banking-mongo-express
restart: always
ports: - "8081:8081"
depends_on: - mongo
environment: - ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME=admin - ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD=password - ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER=mongo - ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_AUTH_USERNAME=admin - ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_AUTH_PASSWORD=password - ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_USERNAME=admin - ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD=password
networks: - banking-network
networks:
banking-network:
driver: bridge
volumes:
mongodb-data:API Documentation
The application uses Swagger UI for API documentation:
const swaggerOptions = {
definition: {
openapi: '3.0.0',
info: {
title: 'Banking API',
version: '1.0.0',
description: 'API for banking operations'
},
servers: [
{
url: '/api'
}
]
},
apis: ['./src/api/routes/*.ts']
};Testing Strategy
The application includes comprehensive tests:
- Unit Tests: Test individual components in isolation
- Integration Tests: Test interactions between components
- API Tests: Test the API endpoints
Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: UUID Compatibility with MongoDB
MongoDB's ObjectId doesn't match the UUID format used in the domain layer.
Solution: Created a custom UUID field in the MongoDB schema and used it as the reference ID for domain entities.
Challenge: Transaction Consistency
Ensuring that transfers between accounts are atomic.
Solution: Used MongoDB transactions to ensure that both the withdrawal and deposit operations succeed or fail together.
Challenge: Domain Logic vs. Persistence
Keeping domain logic separate from persistence concerns.
Solution: Used the repository pattern to abstract data access and implemented mappers to convert between domain entities and database models.
GitHub Repository
The complete source code for this project is available on GitHub: https://github.com/aamersadiq/node-mongodb
Conclusion
This project showcases how to:
- Implement domain driven design in a Node.js application
- Use TypeScript for type safety and better developer experience
- Work with MongoDB and Mongoose for flexible data storage
- Create a RESTful API with Express
- Document APIs with Swagger
- Containerize applications with Docker
- Implement comprehensive testing strategies
